2.1 KiB
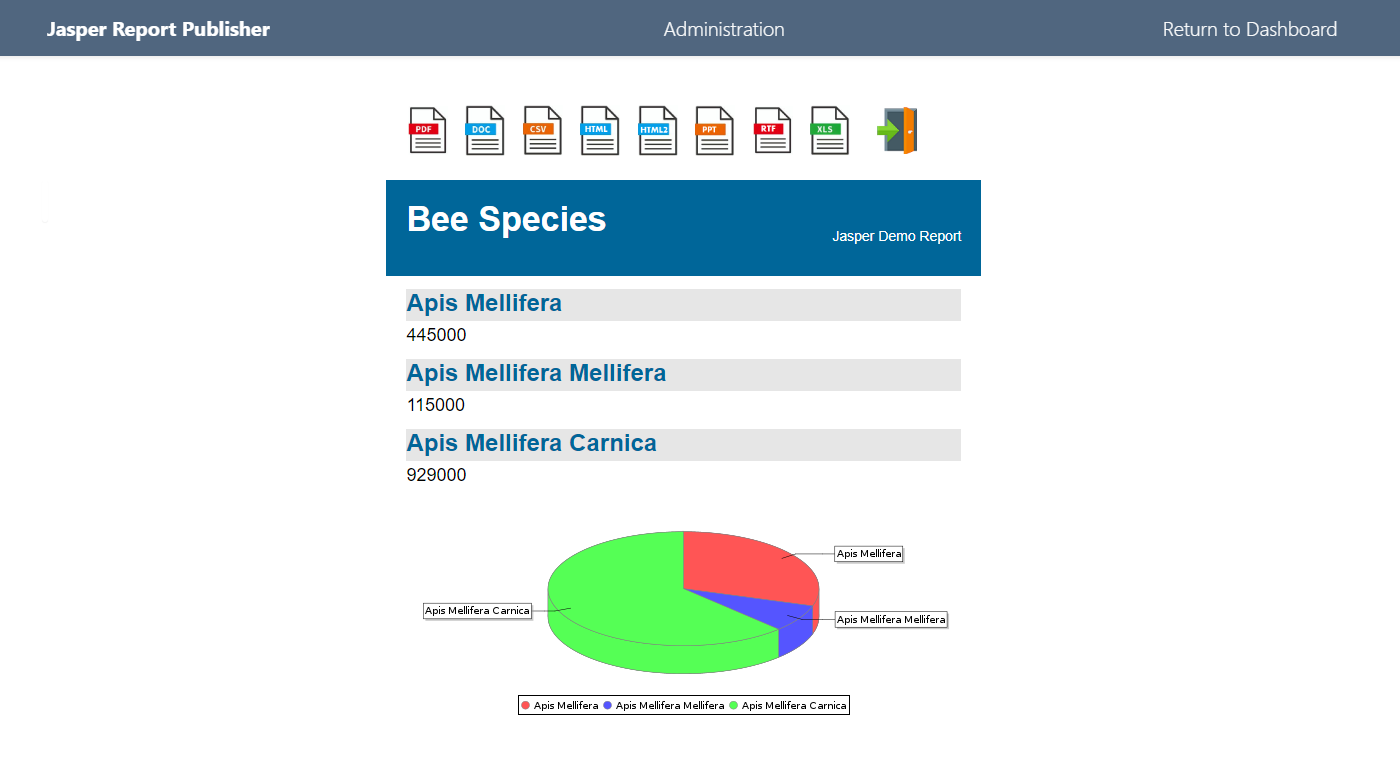
Hot Spot Analysis
Identify statistically significant clusters of high and low values using Getis-Ord Gi* statistics.
Overview
Hot spot analysis uses the Getis-Ord Gi* statistic to identify statistically significant spatial clusters. Features are classified as:
- 99% Hot Spot: Very high values, 99% confidence
- 95% Hot Spot: High values, 95% confidence
- 90% Hot Spot: High values, 90% confidence
- Not Significant: No significant clustering
- 90% Cold Spot: Low values, 90% confidence
- 95% Cold Spot: Low values, 95% confidence
- 99% Cold Spot: Very low values, 99% confidence
Inputs
- Dataset: Point or polygon dataset
- Value Field: Numeric field to analyze
- Neighbor Type: Distance-based or K-nearest neighbors
- Distance (if distance-based): Maximum neighbor distance
- K Neighbors (if KNN): Number of nearest neighbors
Outputs
New dataset containing:
- Original geometry
- Gi Z-Score*: Standardized z-score
- P-Value: Statistical significance
- Hot Spot Class: Categorized class
- Original attributes
Algorithm
- Calculate spatial weights matrix based on neighbor configuration
- Compute Getis-Ord Gi* statistic for each feature
- Calculate z-scores and p-values
- Categorize into hot spot classes
- Store results in output dataset
Example
{
"dataset_id": 123,
"value_field": "population",
"neighbor_type": "distance",
"distance": 1000
}
Background Jobs
This analysis runs as a background job. See Hot Spot Analysis Worker for details.
Use Cases
- Crime analysis
- Disease clustering
- Economic activity patterns
- Environmental monitoring
- Social phenomena analysis
Notes
- Requires numeric field with sufficient variation
- Distance should be appropriate for data scale
- KNN method is generally faster for large datasets
- Results depend on neighbor configuration

 PostGIS
PostGIS Mobile
Mobile QGIS
QGIS MapBender
MapBender GeoServer
GeoServer GeoNode
GeoNode GeoNetwork
GeoNetwork Novella
Novella Solutions
Solutions