8.9 KiB
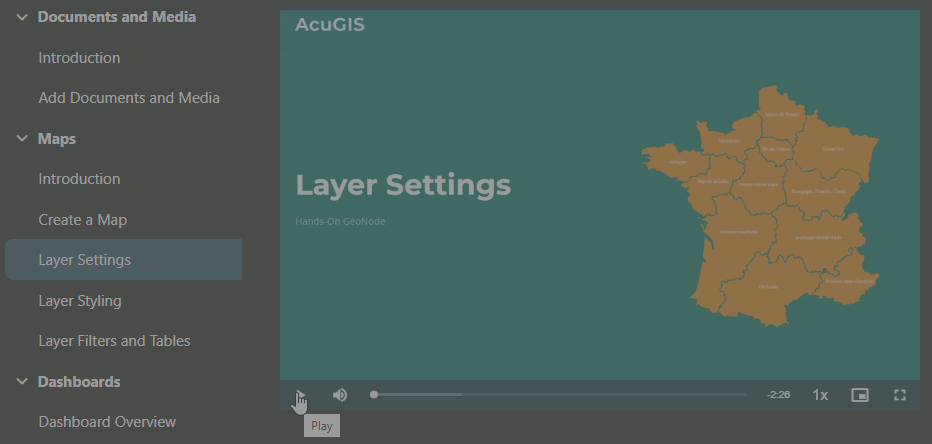
Architecture Overview
This document provides a comprehensive overview of the Aurora GIS architecture, including system components, data flows, and design patterns.
System Architecture
Aurora GIS follows a modular architecture with clear separation between:
- Frontend: PHP-based web interface with JavaScript for interactivity
- Backend: PHP application layer with PostgreSQL/PostGIS database
- Workers: Background job processing system
- API: RESTful API layer for programmatic access
- Analysis Engine: Spatial analysis tools and algorithms
Core Components
1. Dataset Engine
The dataset engine is the core component responsible for managing spatial datasets.
Data Storage Model
Each dataset is stored in its own table following the naming convention spatial_data_{dataset_id}:
CREATE TABLE spatial_data_{id} (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
feature_id TEXT,
geometry_type TEXT,
properties JSONB,
geometry JSONB,
geom GEOMETRY,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW()
);
Benefits:
- Better performance with large numbers of datasets
- Easier data management and cleanup
- Improved query performance for individual datasets
- Reduced table size and index overhead
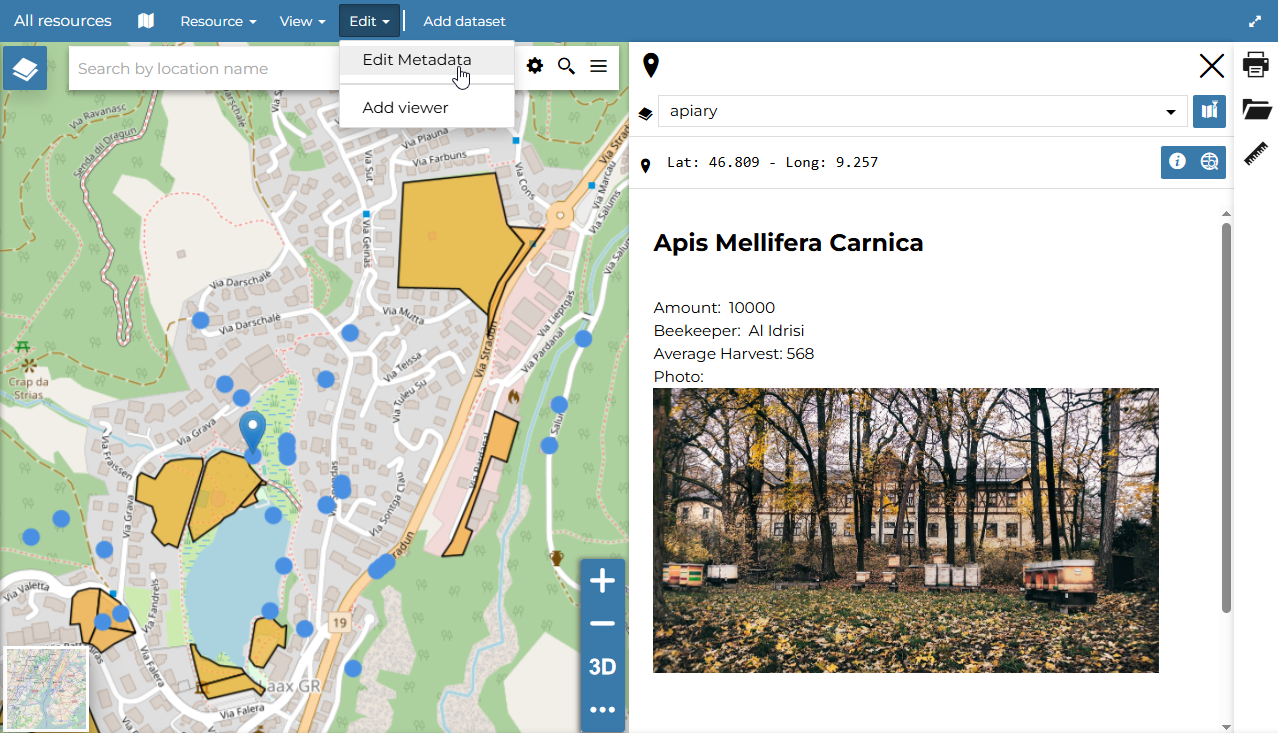
Dataset Metadata
Dataset metadata is stored in the spatial_files table:
- File information (name, path, type, size)
- User-provided description
- Extracted metadata (JSONB)
- Access permissions
- Creation and update timestamps
PostGIS Integration
- All spatial data stored as PostGIS
GEOMETRYtype - Automatic SRID handling (default: 4326)
- Spatial indexes using GiST for performance
- Support for all PostGIS geometry types
2. Background Jobs System
The background jobs system enables asynchronous processing of long-running operations.
Job Queue
Jobs are stored in the background_jobs table:
CREATE TABLE background_jobs (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
user_id INTEGER,
job_type TEXT,
params JSONB,
status TEXT, -- 'queued', 'running', 'completed', 'failed'
result JSONB,
error_message TEXT,
progress INTEGER,
created_at TIMESTAMP,
started_at TIMESTAMP,
finished_at TIMESTAMP
);
Job Lifecycle
- Enqueue: Job created with status 'queued'
- Fetch: Worker fetches next job using
FOR UPDATE SKIP LOCKED - Process: Worker updates status to 'running' and processes job
- Complete: Worker updates status to 'completed' with results
- Error: On failure, status set to 'failed' with error message
Worker Architecture
Workers are long-running PHP CLI scripts that:
- Poll the database for queued jobs
- Process jobs of a specific type
- Handle errors gracefully
- Log progress and results
- Run continuously until stopped
See Workers Documentation for details on each worker.
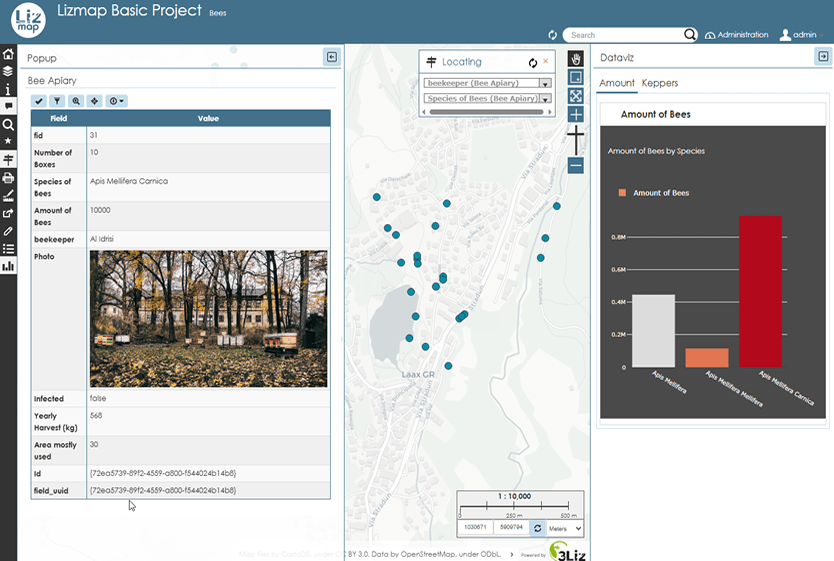
3. Analysis Tools
Aurora GIS provides a comprehensive suite of spatial analysis tools.
Vector Analysis Tools
- Hot Spot Analysis: Getis-Ord Gi* statistics for identifying clusters
- Outlier Detection: Z-score and MAD-based outlier identification
- KDE (Kernel Density Estimation): Density surface generation
- Clustering: Spatial clustering algorithms
- Proximity Analysis: Buffer, nearest neighbor, distance calculations
- Overlay Operations: Intersect, union, erase, join
Raster Analysis Tools
- Zonal Statistics: Calculate statistics within polygon zones
- Raster Histogram: Analyze pixel value distributions
- Raster Summary: Generate summary statistics
- Raster Profile: Extract values along a line
- Raster Conversion: Convert between formats
- Raster Comparison: Compare two raster datasets
See Analysis Tools Documentation for details.
4. API Layer
The API layer provides RESTful access to datasets and analysis tools.
API Structure
- Basic API (
/api/basic/index.php): Dataset listing, details, GeoJSON queries - Server API (
/api/server/index.php): Server information and capabilities - Images API (
/api/images/index.php): GeoServer proxy and catalog - Analysis APIs: Endpoints for running analysis tools
- Worker APIs: Endpoints for job management
Authentication
- Session-based authentication for web interface
- API key authentication (optional)
- Dataset-level access control
- Public dataset access (configurable)
See API Documentation for endpoint details.
5. PostGIS Data Flows
Import Flow
Uploaded File
↓
Format Detection
↓
Geometry Extraction
↓
PostGIS Processing
↓
spatial_data_{id} Table
↓
Spatial Index Creation
↓
Metadata Extraction
↓
spatial_files Record
Analysis Flow
User Request
↓
Job Enqueue
↓
Worker Fetch
↓
PostGIS Analysis
↓
Result Table/View
↓
Job Complete
↓
User Notification
Export Flow
Dataset Selection
↓
Query PostGIS Table
↓
Format Conversion
↓
GeoJSON/Shapefile/CSV
↓
Download
Data Processing Pipeline
File Upload Processing
- File Validation: Check file type, size, and format
- Geometry Extraction: Parse geometry from source format
- SRID Detection: Identify or assign spatial reference system
- Table Creation: Create
spatial_data_{id}table - Data Import: Insert features into PostGIS table
- Index Creation: Create spatial and attribute indexes
- Metadata Extraction: Extract and store metadata
- Registration: Create
spatial_filesrecord
Analysis Processing
- Parameter Validation: Validate input parameters
- Job Creation: Enqueue background job
- Worker Processing: Worker fetches and processes job
- PostGIS Execution: Run spatial analysis queries
- Result Storage: Store results in table/view
- Metadata Update: Update job status and results
- User Notification: Notify user of completion
Database Schema
Core Tables
- spatial_files: Dataset metadata and file information
- spatial_data_{id}: Individual dataset tables (dynamic)
- background_jobs: Job queue and status
- user: User accounts and authentication
- access_group: Access control groups
- user_access: User-group associations
- dataset_permissions: Dataset-level permissions
Supporting Tables
- ogc_connections: External PostGIS connections
- scheduled_imports: Scheduled URL imports
- map_views: Saved map configurations
- dashboards: Dashboard definitions
- presentations: Presentation configurations
- categories_keywords: Dataset categorization
Security Architecture
Authentication
- Session-based authentication
- OAuth support (GitHub, Google, Microsoft)
- Password hashing (bcrypt)
- Session management
Authorization
- Role-based access control (Admin, User, Publisher)
- Dataset-level permissions
- Access group management
- Public dataset access (optional)
Data Security
- SQL injection prevention (prepared statements)
- XSS protection (output escaping)
- File upload validation
- Path traversal prevention
- Secure file storage
Performance Optimizations
Database Optimizations
- Spatial indexes (GiST) on geometry columns
- Attribute indexes on frequently queried fields
- Connection pooling (PgBouncer support)
- Query optimization and caching
- Materialized views for complex queries
Application Optimizations
- Lazy loading of map components
- Pagination for large datasets
- Background job processing
- Caching of metadata and configurations
- Efficient JSONB storage
Worker Optimizations
- Parallel job processing (multiple workers)
- Job prioritization
- Resource limits and timeouts
- Error handling and retry logic
Scalability Considerations
Horizontal Scaling
- Stateless application design
- Database connection pooling
- Worker scaling (multiple worker instances)
- Load balancing support
Vertical Scaling
- Database query optimization
- Index optimization
- Memory management
- Worker resource allocation
Integration Points
External Services
- GeoServer: WMS/WFS services
- QGIS Server: QGIS project rendering
- pg_tileserv: Vector tile generation
- OAuth Providers: Authentication
- S3: Cloud storage for large files
Data Sources
- PostGIS Remote: External PostGIS databases
- URL Imports: Web-accessible spatial data
- File Uploads: Local file uploads
- Overture Maps: Parquet file imports
- S3 Buckets: Cloud-based data sources
Monitoring and Logging
Application Logging
- Error logging to files
- Worker-specific logs
- Import operation logs
- API access logs
Database Monitoring
- Query performance monitoring
- Connection pool monitoring
- Table size monitoring
- Index usage statistics

 PostGIS
PostGIS Mobile
Mobile QGIS
QGIS MapBender
MapBender GeoServer
GeoServer GeoNode
GeoNode GeoNetwork
GeoNetwork Novella
Novella Solutions
Solutions