raster2pgsql¶
Table of Contents
Create Extension¶
In order to use raster2pgsql, either by command line or the control panel, you will need to create the postgis_raster extension
su to postgres
root@demo:# su - postgres
Start psql
postgres@demo:~$ psql
psql (15.3 (Ubuntu 15.3-1.pgdg22.04+1))
Type "help" for help.
Connect to target database (in this case, postgisftw)
postgres=# \c postgisftw
You are now connected to database "postgisftw" as user "postgres".
Issue the create extension command
postgisftw=# create extension postgis_raster;
CREATE EXTENSION
postgisftw=#
raster2pgsql Loader¶
An included raster2pgsql tool is available if you installed Webmin.
There are 2 options for loading raster files:
- Load using the raster2pgsql File Loader.
- Load using raster2pgsql via command line.
Load via raster2pgsql Loader¶
Click the Shape File Loader tab as shown below
The load options are displayed below.
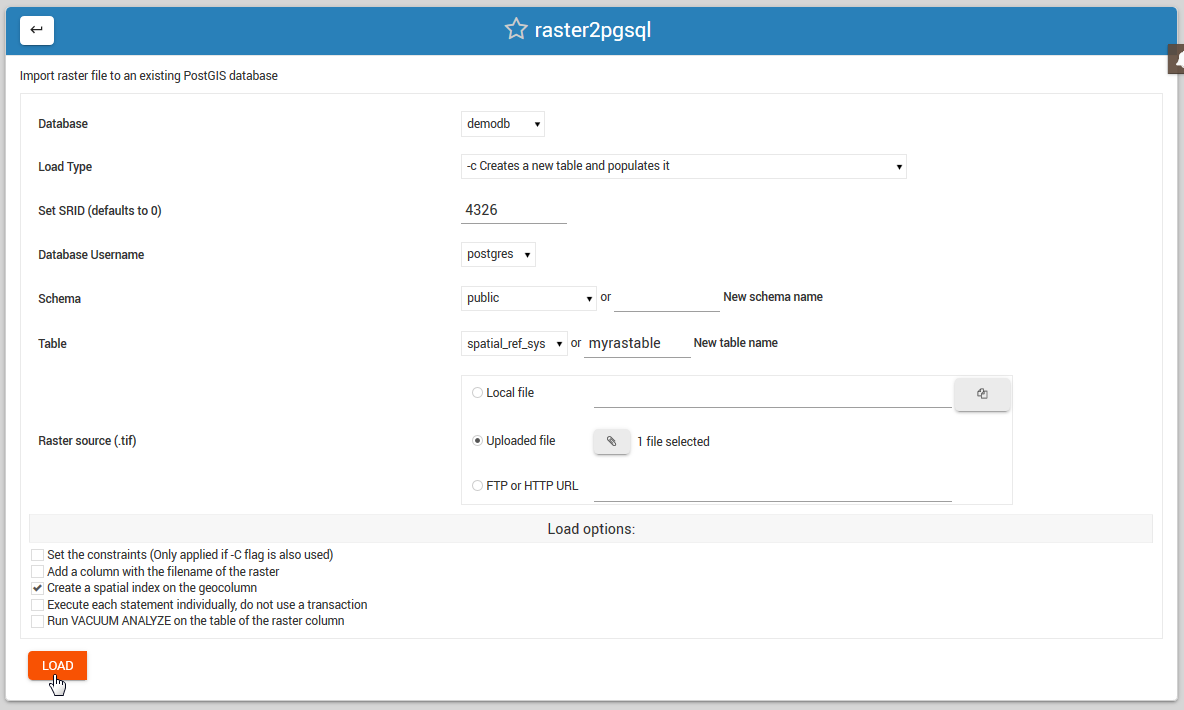
Also select if load will be into a new Schema and, in the case of New Table creation, the table name to be created.
Load Options
Database: select the database you wish to load the shape file to.
Load Type: Create, Drop, Append, or Prepare
Set SRID: Defaults to 0 if not set
Database Username: Select the user who will own the data
Schema: Select an existing schema or create a new schema.
Table: Select an existing table or create new one
Raster File Source: Local, Upload, or FTP/HTTP
Load via Comamnd Line¶
Usage
raster2pgsql usage can be found using the ‘raster2pgsql’ command.
[root@postgis ~]# raster2pgsql
RELEASE: 3.0.1 GDAL_VERSION=30 (ec2a9aa)
USAGE: raster2pgsql [<options>] <raster>[ <raster>[ ...]] [[<schema>.]<table>]
Multiple rasters can also be specified using wildcards (*,?).
OPTIONS:
-s <srid> Set the SRID field. Defaults to 0. If SRID not
provided or is 0, raster's metadata will be checked to
determine an appropriate SRID.
-b <band> Index (1-based) of band to extract from raster. For more
than one band index, separate with comma (,). Ranges can be
defined by separating with dash (-). If unspecified, all bands
of raster will be extracted.
-t <tile size> Cut raster into tiles to be inserted one per
table row. <tile size> is expressed as WIDTHxHEIGHT.
<tile size> can also be "auto" to allow the loader to compute
an appropriate tile size using the first raster and applied to
all rasters.
-P Pad right-most and bottom-most tiles to guarantee that all tiles
have the same width and height.
-R Register the raster as an out-of-db (filesystem) raster. Provided
raster should have absolute path to the file
(-d|a|c|p) These are mutually exclusive options:
-d Drops the table, then recreates it and populates
it with current raster data.
-a Appends raster into current table, must be
exactly the same table schema.
-c Creates a new table and populates it, this is the
default if you do not specify any options.
-p Prepare mode, only creates the table.
-f <column> Specify the name of the raster column
-F Add a column with the filename of the raster.
-n <column> Specify the name of the filename column. Implies -F.
-l <overview factor> Create overview of the raster. For more than
one factor, separate with comma(,). Overview table name follows
the pattern o_<overview factor>_<table>. Created overview is
stored in the database and is not affected by -R.
-q Wrap PostgreSQL identifiers in quotes.
-I Create a GIST spatial index on the raster column. The ANALYZE
command will automatically be issued for the created index.
-M Run VACUUM ANALYZE on the table of the raster column. Most
useful when appending raster to existing table with -a.
-C Set the standard set of constraints on the raster
column after the rasters are loaded. Some constraints may fail
if one or more rasters violate the constraint.
-x Disable setting the max extent constraint. Only applied if
-C flag is also used.
-r Set the constraints (spatially unique and coverage tile) for
regular blocking. Only applied if -C flag is also used.
-T <tablespace> Specify the tablespace for the new table.
Note that indices (including the primary key) will still use
the default tablespace unless the -X flag is also used.
-X <tablespace> Specify the tablespace for the table's new index.
This applies to the primary key and the spatial index if
the -I flag is used.
-N <nodata> NODATA value to use on bands without a NODATA value.
-k Skip NODATA value checks for each raster band.
-E <endian> Control endianness of generated binary output of
raster. Use 0 for XDR and 1 for NDR (default). Only NDR
is supported at this time.
-V <version> Specify version of output WKB format. Default
is 0. Only 0 is supported at this time.
-e Execute each statement individually, do not use a transaction.
-Y Use COPY statements instead of INSERT statements.
-G Print the supported GDAL raster formats.
-? Display this help screen.
Troubleshooting¶
If the above commands produce ‘raster2pgsql command not found’, close your existing SSH session and create a new one.
Documentation¶
Below are resources to get started with ogr2ogr and gdal_translate: